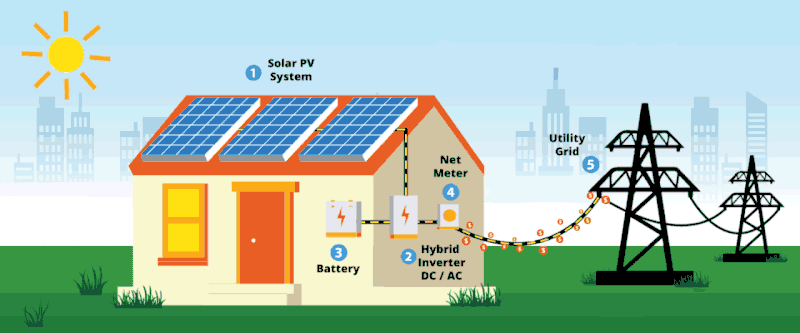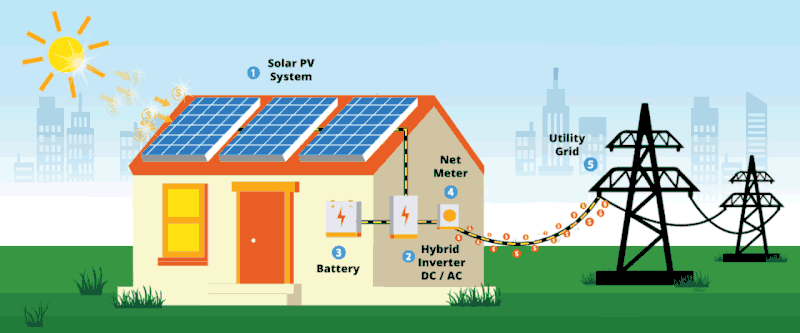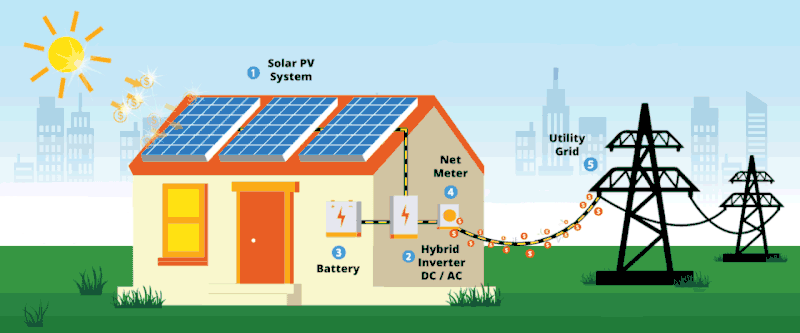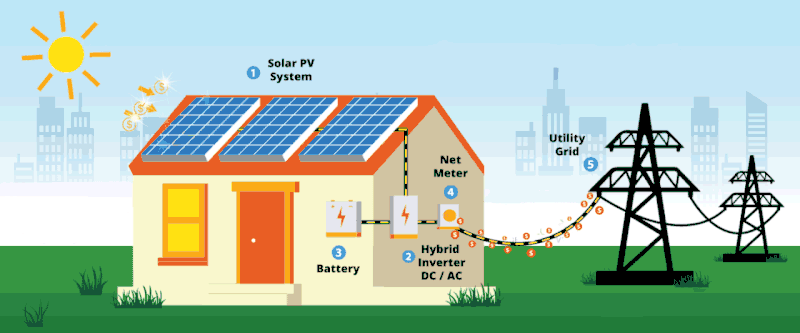
Solar energy is no longer a future idea. It is already reshaping how homes and businesses power their daily operations. Here are 10 solar facts many people in Kenya still find surprising.
1. Solar works even on cloudy days: Panels do not need direct sunlight to generate power. They still produce electricity under cloud cover, just at a lower output.
2. Kenya has some of the best solar potential in the world: Most regions receive strong sunlight for most of the year, making solar systems highly efficient locally.
3. Solar can reduce electricity bills immediately: Savings start from the first month after installation, not years later.
4. Businesses benefit more than homes: Daytime operations align perfectly with solar production, which maximizes savings for commercial users.
5. Solar systems require minimal maintenance: Regular cleaning and basic checks are often enough to keep systems running efficiently for years.
6. Batteries are not always necessary: Grid-tied and hybrid systems can work without batteries, depending on usage and reliability needs.
7. Solar increases property value: Homes and commercial buildings with solar systems are more attractive to buyers and tenants.
8. Solar protects against power outages: With storage or hybrid systems, operations can continue even during blackouts.
9. Financing options make solar more accessible: Models like lease-to-own and power purchase agreements reduce upfront costs for businesses.
10. Solar is a long-term investment, not an expense: Most systems pay for themselves over time while continuing to generate free energy.
If you are considering solar for your home or business, now is a good time to start the conversation.